Protein Expression after Stereotatic radiosurgery
Abnormal brain blood vessel architecture as in the case of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are at increased risk of rupture causing a haemorrhage and possible death. The two treatment options involve surgical removal or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for difficult to access deep AVMs. This study tested the hypothesis that SRS would promote relocation of some proteins to the cell surface of irradiated cells, allowing them to be targeted by specific affinity reagents. Biotinylated cell surface proteins were captured following treatment and LC-MS/MS and SWATH analysis conducted to identify these molecules. Interestingly, compared to control cells, several mitochondrial and cytoskeletal proteins appeared to be externalized following treatment. Immunocytochemistry confirmed these findings. The paper paves the way for follow-up in vivo studies in AVM model animals.
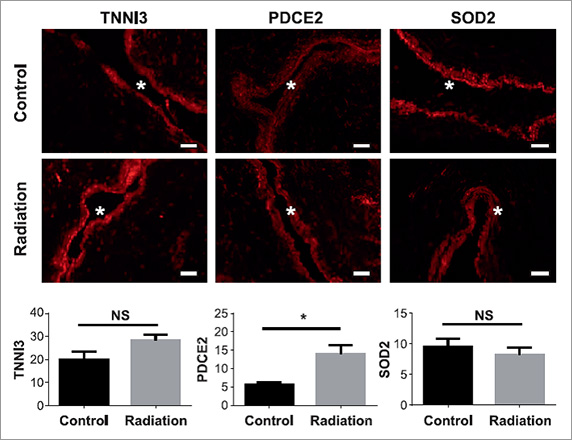
Image: McRobb et al. Radiat. Res. 2017.
McRobb LS, Lee VS, Simonian M, Zhao Z, Thomas SG, Wiedmann M, Raj JV, Grace M, Moutrie V, McKay MJ, Molloy MP, Stoodley MA. Radiosurgery Alters the Endothelial Surface Proteome: Externalized Intracellular Molecules as Potential Vascular Targets in Irradiated Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Radiat. Res. 2017 Jan; 187(1):66-78.