Amino Acid Analysis - Services
- Amino acid profile – our standard AAA assay for quantifying the total amino acid content of 18 common (or proteinogenic) amino acids in a sample. See list below. The assay uses liquid 6M HCl to acid hydrolyse the sample into individual amino acids. This, however, converts glutamine and asparagine to their respective acids, glutamic acid and aspartic acid, and destroys or partly destroys cyst(e)ine and tryptophan.
That is, the reported amount for:
glutamic acid = glutamine + glutamic acid (also called Glx)
aspartic acid = asparagine + aspartic acid (also called Asx) - Amino acid profile with hydroxyproline and taurine – the same assay as amino acid profile but two extra amino acids commonly found in animal food products are also quantified. Hydroxyproline is a post-translation modification of proline and is a major component of collagen. Because of the high abundance of collagen, hydroxyproline significantly comprises roughly 4% of all amino acids found in animal tissue.
Taurine is chemically different to other amino acids in that it contains a sulfonic acid rather than a carboxylic acid. Note, it is not incorporated into protein and can be analysed either as part of this assay or as a free amino acid. It is an essential amino acid for cats. - High sensitivity AAA – this is an assay for purified protein samples and quantifies the total amino acid profile (as in 1. above) but at higher sensitivity. It only requires approximately 5 microgram of sample. It hydrolyses samples using gas-phase HCl and so converts converts glutamine and asparagine to their respective acids, glutamic acid and aspartic acid, and destroys or partly destroys cyst(e)ine and tryptophan.
That is, the reported amount for:
glutamic acid = glutamine + glutamic acid (also called Glx)
aspartic acid = asparagine + aspartic acid (also called Asx)This procedure is used for the amino acid analysis of biopharmaceuticals.
- Tryptophan analysis - Tryptophan is an essential amino acid in animals and is often the least abundant amino acid in protein material. Total tryptophan is measured after performing alkaline hydrolysis in 5M NaOH as it is labile to strong acid conditions. That is, it requires a separate analysis from the other amino acids.
- Total Cys (cysteine + cystine) analysis - cysteine is unstable at physiological pH and readily converts to its disulphide form cystine (also called the dimer or oxidised form) and is generally found as cystine in proteins. To analyse total cys (cysteine + cystine) it necessary to convert it to the more stable cysteic acid by oxidation with performic acid and then perform acid hydrolysis followed by cysteic acid quantitation. By convention it is reported as cysteine content .
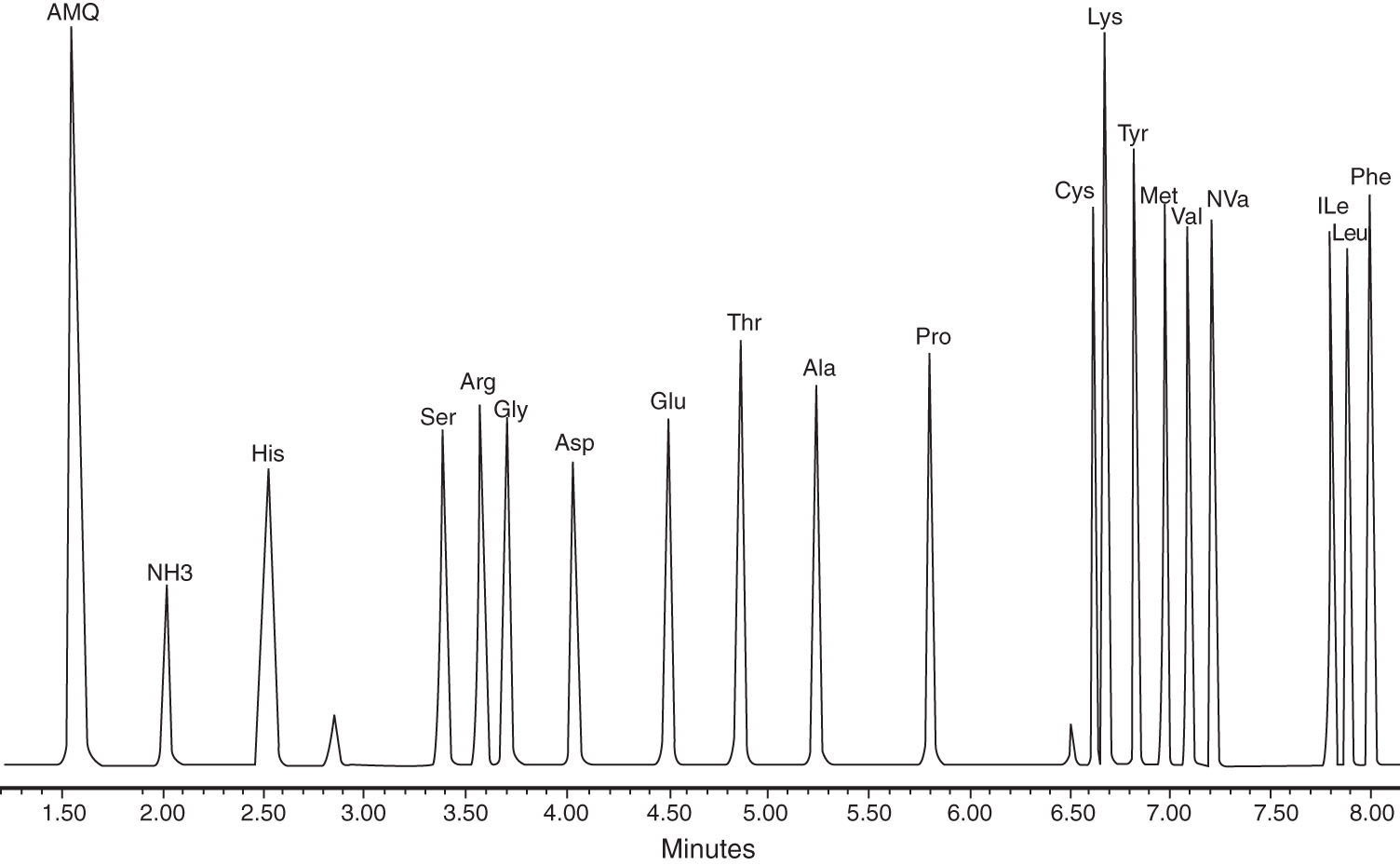
- Free amino acid profile – this assay separates and quantifies the free amino acids only. That is, does not analyse any amino acids contained in proteins or peptides. The standard assay analyses for the 20 common (or proteinogenic amino acids). Extra amino acids such as GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid) and taurine may be added to the analysis if requested. For solid samples an appropriate extraction method will be applied.
- Physiological or plasma amino acid profile – we specialise in analysing plasma for free amino acids and have developed procedures to analyse up to 36 amino acids in a single run (see figure in newsletter). The assay has been successfully used to analyse amino acids in human, mouse, poultry, pig and sheep and resulted in many published articles.
- Aminothiol analysis –aminothiol containing compounds play important roles in cellular metabolism and are vital components of most cell culture media. We have developed an assay based on SBD-F reagent to fluorescently tag the thiol group and then separate and quantify by UPLC. The assay can be used to determine homocysteine (Hcy), cysteine/cystine (Cys), N-acetylcysteine (NAC), cysteinylglycine (CysGly), and glutathione (GSH) in plasma or culture media.
- Glutamine/Asparagine – procedures are available to analyse for protein-bound glutamine and asparagine using an enzyme hydrolysis methodology. This procedure may also be applied to other acid-labile amino acids, such as, methionine sulfoxide and cross-linked amino acids.
- Other amino acids – there are procedures available to analyse for less common amino acids such as ornithine, citrulline, beta-alanine, AABA, hydroxylysine, methylhistidine, theanine, lanthionine and many others. Methods may be able to be developed to analyse for other unusual amino acid. Please feel free to make an enquiry.