APAF Newsletter Vol. 6 No. 2
Welcome to APAF's second 2016 newsletter.
In this issue we discuss research on novel bioactives in spider venoms with Professor Glenn King and his colleagues from The University of Queensland's Centre of Pain Research within the Institute for Molecular Bioscience. We also highlight the use of Multiplex Bead-based assays to quantitate proteins in biological fluids associated with cancer, metabolism, inflammation and signaling. A range of multiplexed assays are available for human, mouse, rat and dog.
The role of bioinformatics in biological research cannot be understated and APAF’s bioinformatics team is highly skilled to provide statistical and computational support to value-add to your project. Please review our Bioinformatics page for more information.
APAF would like to take this opportunity to thank all our users for your support in 2016 and we look forward to being of further assistance in 2017.
N-Terminal Sequencing uncovers selective sodium ion channel bioactives

More effective analgesics with fewer side-effects are required to treat chronic pain. In conjunction with Professor Glenn King and colleagues at the University of Queensland’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience, APAF has been a longer-term partner in determining venom peptide primary structures through Edman sequencing. Recently, the team reported the discovery of Tp1a, a novel NaV1.7 inhibitor from the venom of a Peruvian tarantula. Read more.
Multiplex Assays of Biological Fluids
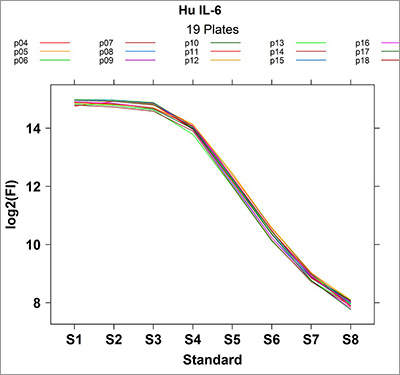
Multiplexed immuno assays (MIA) are conducted using the Bio-Plex/Luminex suspension array system as a plate reader and epMotion robotic workstation for liquid delivery for precision and reproducibility of the MIA assays. MIA is predominately performed for measuring concentrations of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, phosphoproteins, and many other human disease specific assays such as cancer biomarker panels, diabetes, metabolic, hormonal, inflammation, cell signalling, kidney toxicity, acute phase, isotyping, etc. from body fluids, cell culture supernatants and tissue samples. In addition to human assays there are several animal assays are available such as canine kidney toxicity, mouse and rat cytokines, etc. MIA is performed at APAF using commercially available assay kits only. There are numerous analytes from different companies who makes kits for MIA partnering with Luminex. Read more
New Web site that is mobile friendly
APAF has recently evolved its website, making it mobile friendly for phones and tablets. Our website can be accessed from our longstanding URL at www.proteome.org.au or www.apaf.com.au. We welcome feedback on ease of use to improve the experience. While you will continue to find the important information associated with proteomic techniques, we have also organised the features into research discipline areas including Biomedical, Agricultural and Analytical, representing groupings of our client base. Our Bioinformatics section has also been expanded to better showcase our support in this area.