Amino Thiols
Measuring Aminothiols reduced and oxidised
Increases in the concentrations of the thiol compounds glutathione (GSH), cysteine (Cys), and homocysteine (HCys) are correlated with several diseases, including cardiovascular, atherosclerosis, and chronic kidney disease. These aminothiols possess anti-oxidative and auto-oxidative properties and perform several vital functions in cells.
Numerous separation techniques, including gas chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography, and capillary electrophoresis, have been developed for the determination of thiol compounds in biological samples.
APAF Staff have developed an Ultra Pressure Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) method for measuring these aminothiols in their reduced and oxidised forms. We developed this methodology in response to a request to measure N-Acetyl-Cysteine which is used in a number of clinical conditions and in areas such as sports physiology.
Our internal standards enable us to establish that the samples have been successfully reduced. We then label the amino thiols and run on a UPLC with fluorescent detection. Aminothiols Glutathione, Cysteine and Homocysteine are the first line of defence against oxidants. As such they can be used to monitor oxidative stress and can also monitor vascular injury. They also play an important role in cell signalling, metabolism and detoxification. Cysteine, which is a metabolite of homocysteine and a precursor of glutathione, is the most abundant thiol in plasma.
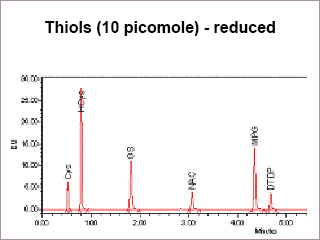
The Chromatograph below shows the separation of 6 reduced Thiols in under 5 minutes. For information on pricing and samples we can use contact APAF.